
Gift-giving and celebrations are ubiquitous human traditions that are profoundly ingrained in the social fabric of cultures across the globe. The customs, meanings, and styles of these practices differ significantly between societies, despite the fact that the joy of marking special occasions and exchanging presents is shared globally. Our understanding of the ways in which individuals express gratitude, strengthen relationships, ...
The internet has revolutionized the manner in which individuals worldwide connect, communicate, and consume information. Nevertheless, the prevalence of social media and internet use varies substantially among various regions, as they are influenced by a variety of factors, including infrastructure, culture, economic development, and government policies. Comprehending these distinctions illuminates the distinctive methods by which individuals worldwide interact online and ...

Pets are cherished by a significant number of individuals worldwide; however, the perception and function of animals as companions can differ significantly across different cultures. In Western countries, pets are frequently perceived as cherished family members, sources of emotional support, and acquaintances. Affection and companionship are not entirely absent in numerous ASEAN nations; however, animals are generally employed for more ...

The definition of a happy existence is subject to significant variation in the fast-paced world of today. A tension between materialism, which is the pursuit of wealth and possessions, and simplicity, which is the desire for a life focused on essentials, relationships, and interior contentment, often rests at the heart of these differences. This equilibrium fluctuates across cultures in response ...

Although time is a universal concept, the manner in which individuals perceive and regulate it varies significantly across different cultures. One of the most apparent contrasts is the Western emphasis on punctuality and the more adaptable approach that is prevalent in numerous ASEAN countries. These varying perspectives on time have an impact on the pace of life, social interactions, commerce, ...

Cryptocurrencies have progressed significantly since their inception as a specialized digital asset. Presently, they are altering the attitudes of individuals toward financial freedom, payments, and money. One of the most thrilling opportunities is the utilization of cryptocurrencies for significant purchases and services, such as the acquisition of residences and vehicles and the payment for professional services. The future holds the ...

Driven by the proliferation of cryptocurrencies, the automotive sector is on the cusp of a digital payment revolution. The potential of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital currencies to revolutionize the way people purchase motorcycles and automobiles is becoming increasingly apparent as they gain traction on a global scale. Cryptocurrencies provide a variety of benefits, including transnational payments and quicker transactions, ...

At one time, the notion of purchasing a property with Bitcoin appeared to be a futuristic concept that was exclusively designated for early crypto adopters and tech enthusiasts. Nevertheless, the occurrence of purchasing real estate with digital currency is becoming increasingly prevalent as Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies gain mainstream recognition. The Reasons for the Increase in Interest in Bitcoin in ...

Since their inception, cryptocurrencies have gone from being digital anomalies to being recognized assets in the financial world. They have come a long way. However, despite their increasing prominence as investment vehicles, many individuals continue to question whether cryptocurrencies will be truly beneficial for commonplace real-world purchases. The response is contingent upon a combination of regulatory developments, technological advancements, and ...
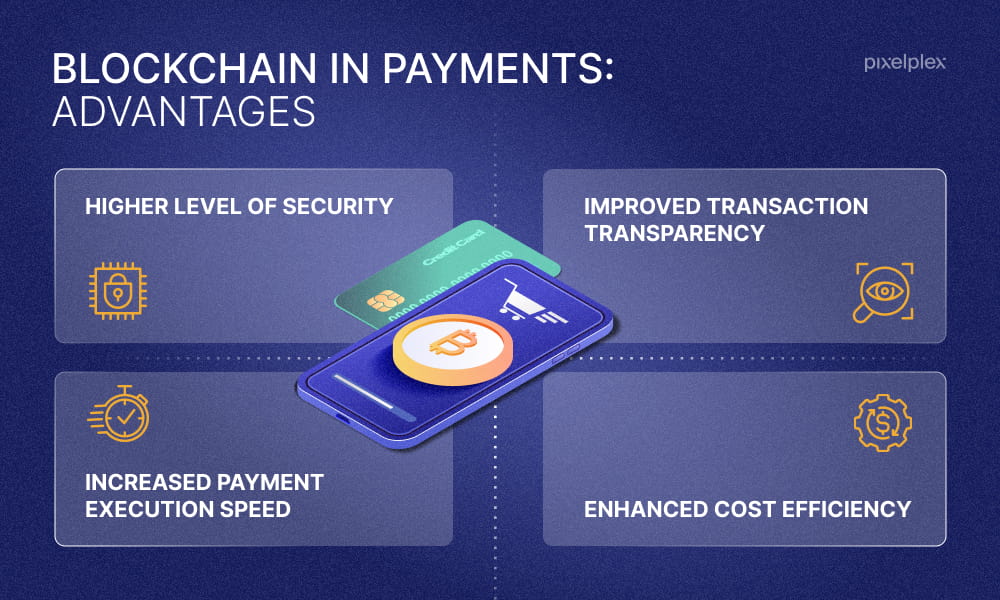
In recent years, cryptocurrency has experienced substantial growth, transitioning from a niche digital asset to a recognizable method of value transmission. One area that is garnering increasing attention is the utilization of crypto payments for significant transactions, such as real estate, prestige vehicles, and high-value business agreements. However, what is the current practicality of cryptocurrencies for such significant expenditures, and ...